Introduction
In essence, the primary contrast between connection-oriented and connectionless services lies in their approach to data transmission. Connection-oriented services entail establishing a connection prior to transmitting data, while connectionless services bypass this connection setup phase entirely. TCP exemplifies a connection-oriented protocol, whereas UDP operates as a connectionless protocol. This article delves into a comprehensive exploration of the disparities between these two types of services.
Table of Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Services
Connection-Oriented Services
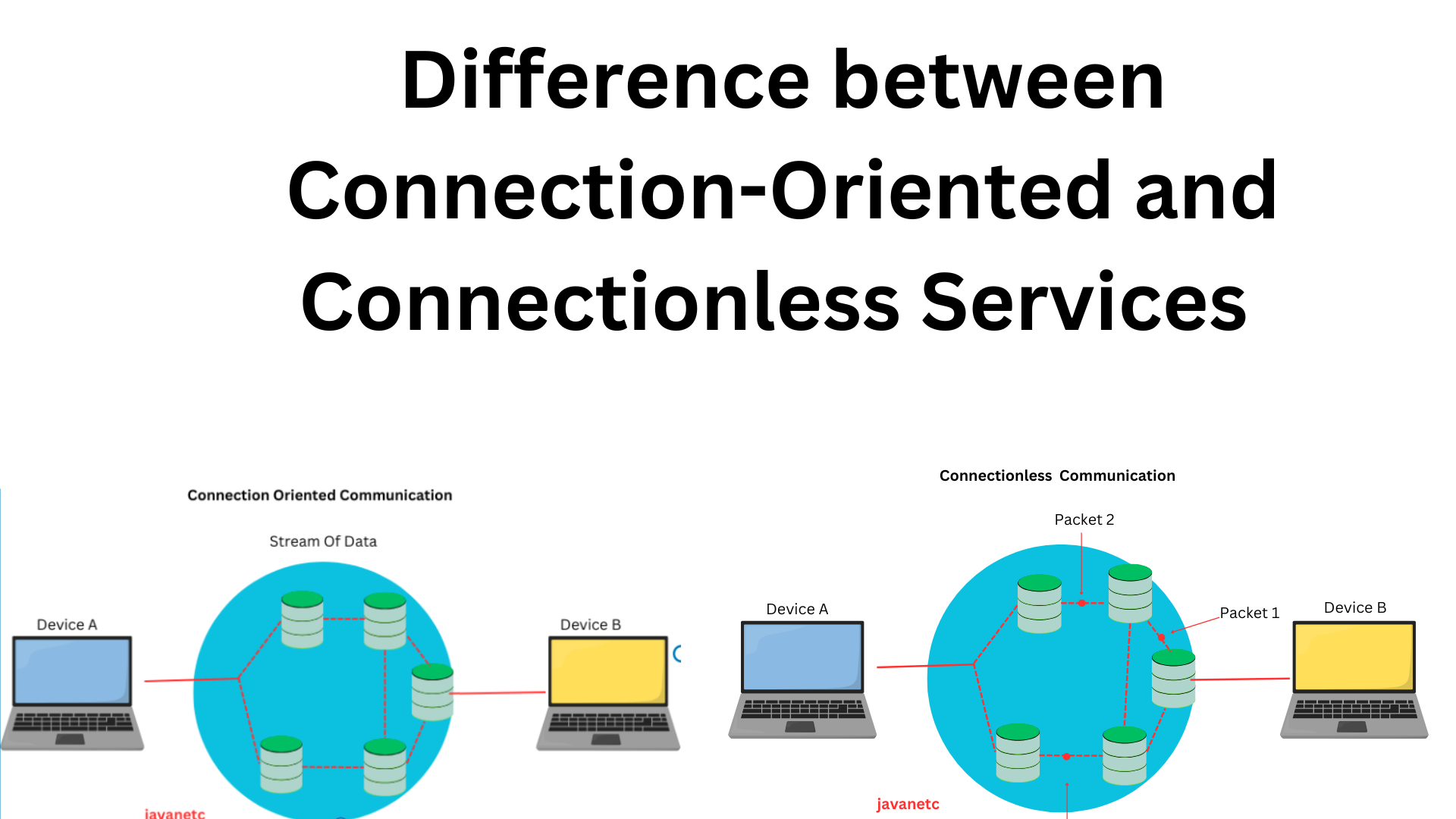
In connection-oriented services, each packet is assigned to a specific source/destination connection, forming what is known as a virtual circuit. This ensures that all packets follow the same route, facilitating reliable data transfer. Such services provide end-to-end connections, which are dedicated links established for data transmission. They also maintain the order of delivery, eliminating any possibility of missing or duplicating information. Additionally, connection-oriented services prevent congestion in the receiving device buffer and communication channel. A typical example of a connection-oriented service is mobile connections.

What is TCP?
TCP, short for Transmission Control Protocol, is a connection-oriented protocol facilitating communication between two or more devices across diverse or similar networks. It utilizes the Internet Protocol (IP) for data transmission between endpoints, hence often denoted as TCP/IP. TCP guarantees the establishment and maintenance of connections throughout the entire data transfer process between senders and receivers.
Connectionless Services
In connectionless services, routers handle each packet independently, potentially directing them along different routes based on router decisions. Unlike connection-oriented services, there’s no assurance of data delivery from sender to receiver. Data intended for transmission is fragmented into packets, each referred to as a datagram, with no guarantee of ordered delivery. Congestion in data transmission between sender and receiver is possible. Packets contain the destination device address, akin to how the postal system operates.

What is UDP?
UDP, or User Datagram Protocol, operates as a connectionless protocol facilitating data transfer between sender and receiver without requiring connection establishment. Senders transmit packets along with destination addresses, but UDP does not guarantee delivery of data packets to the correct destination, nor does it generate acknowledgments for sent data or provide acknowledgments to receivers. Consequently, UDP is classified as an unreliable protocol.
Difference between Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Services
Below is a revised table outlining the variances between: Connection-Oriented and Connectionless Services
| Sr No | Comparison Parameter | Connection-oriented Service | Connectionless Service |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Related System | Developed based on telephone system workings | Developed based on postal system workings |
| 2 | Definition | Establishes end-to-end connection before data transmission | Does not establish any connection prior to data exchange |
| 3 | Virtual path | Creates virtual path/connection between sender and receiver | Does not create virtual path/connection |
| 4 | Authentication | Requires authentication before data transmission | Does not require authentication before data transmission |
| 5 | Data Packets Path | Maintains order of sent data packets | Order of sent data packets not maintained |
| 6 | Bandwidth Requirement | Requires higher bandwidth for transmission | Requires lower bandwidth for transmission |
| 7 | Data Reliability | Guarantees data transfer, hence reliable protocol | Does not guarantee data transfer, hence unreliable |
| 8 | Congestion | No congestion due to end-to-end connection | Congestion possible due to lack of end-to-end connection |
| 9 | Examples | TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) | IP (Internet Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) |
| 10 | Application in the real-world | Text communication, HTTP, SMTP | Video conferencing apps like Zoom, Skype, Gmeet |
Conclusion
In summary, connection-oriented services designate every packet to a specific source/destination connection, whereas connectionless services treat each packet individually. TCP, or Transmission Control Protocol, functions as both a connection-oriented and connectionless protocol, while UDP, or User Datagram Protocol, operates solely as a connectionless protocol.
The primary disparity between connection-oriented and connectionless services lies in their approach to data transmission. Connection-oriented services establish an end-to-end connection, ensuring reliability and preventing congestion. Conversely, connectionless services do not establish such connections, potentially leading to congestion during transmission.



hamir salvachua